For educators in Conservation Biology, Ecology, and Environmental Science, the challenge is often the same: How do we move students from memorising static definitions of "carrying capacity" or "trophic cascades" to understanding them as dynamic, emergent properties of a complex system?
Textbooks are linear, but ecosystems are non-linear. To bridge this gap, inquiry-based learning requires tools that allow students to experiment with the physics of an ecosystem, not just observe it.
Introducing the Ecosystem Safari Simulator: a free, browser-based Agent-Based Model (ABM) designed specifically for the undergraduate and high-school classroom. Unlike standard educational games, which function as "black boxes," this tool offers a transparent, data-driven sandbox for exploring Social-Ecological Systems (SES).
More Than a Game: A Conceptual Agent-Based Model
At its core, the simulator is a robust Agent-Based Model. It instantiates individual agents (Lions, Elephants, Zebras) with heterogeneous internal states—hunger, mating cooldowns, and detection radii.
By manipulating policy levers (such as Predation Rates or Culling Quotas), students are not merely "playing"; they are acting as managers in a coupled human-natural system. They can directly test hypotheses related to:
- Trophic Cascades & Keystone Species: Observe bottom-up collapse caused by mega-herbivore overpopulation (the "Kruger Elephant Dilemma").
- Functional Response: Manipulate predator efficiency to see density-dependent vs. policy-driven population crashes.
- Social-Ecological Systems (SES): Uniquely, this model simulates the friction between ecological boundaries and social rules. Students can analyze the consequences of ignoring management quotas, observing how sustainable interventions can degrade into systemic failure triggered by the violation of social constraints (laws) rather than biological limits.
The "Glass Box" Approach: The Technical Manual
Serious inquiry requires rigorous instructional design. We believe educators must have full visibility into the algorithms governing the simulation to design meaningful experiments.
We are releasing a comprehensive Technical Manual (PDF) for lecturers and experiment planners. This document provides a "glass box" view of the model, detailing the exact finite state machines (FSMs), probabilistic triggers, and hard-coded rules that drive the simulation.
Download the Technical Manual to access:
- Complete Parameter Tables: See the exact speed ranges, reproduction coefficients, and metabolic costs for every species.
- Code-Level Logic: Understand the algorithmic distinctions between passive preservation strategies and active conservation management.
- Experimental Design Guide: Ready-to-use methodology for running rigorous classroom experiments, such as testing the resilience of biodiversity under different management regimes.
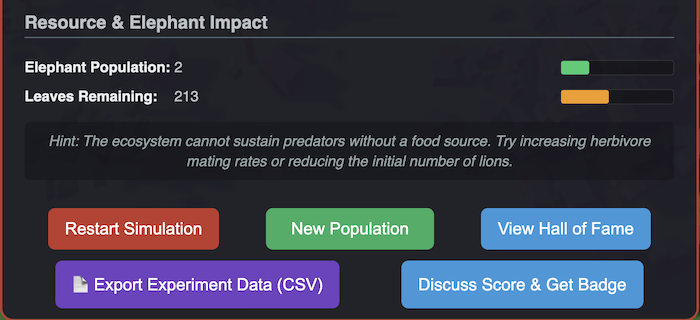
From Observation to Analysis: The CSV Data Export
The most significant feature for researchers and educators is the quantitative Data Logger.
We have moved beyond simple "high scores." The simulation now features a CSV Export functionality that records the state of the system at every simulated day.
When a simulation ends (whether through stability or collapse), students can export a raw dataset containing:
- Time-Series Population Data: Track the exact count of every species day by day.
- Flow Metrics: Analyse cumulative predation events, birth rates, and hunting statistics.
- Policy Inputs: Correlate changes in student interventions (slider movements) with lagged ecological responses.
This feature transforms the activity from a qualitative observation into a Quantitative Data Science Project. Students can import their unique simulation runs into Excel, R, or Python to visualise Lotka-Volterra cycles, identify tipping points, and perform statistical analysis on their management strategies.
Bring the Savannah to Your Classroom
The Ecosystem Safari Simulator offers a unique opportunity to teach Computational Thinking in Biology. By combining an engaging 3D visualization with rigorous documentation and raw data export, it empowers students to stop acting as passive observers and start thinking like systems ecologists.



