The 4 species and 5 sub species of giraffe explained
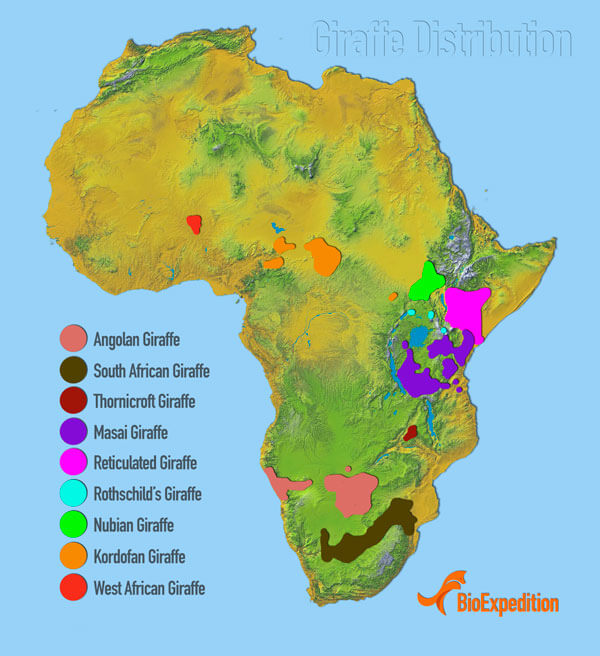
Giraffe Distribution
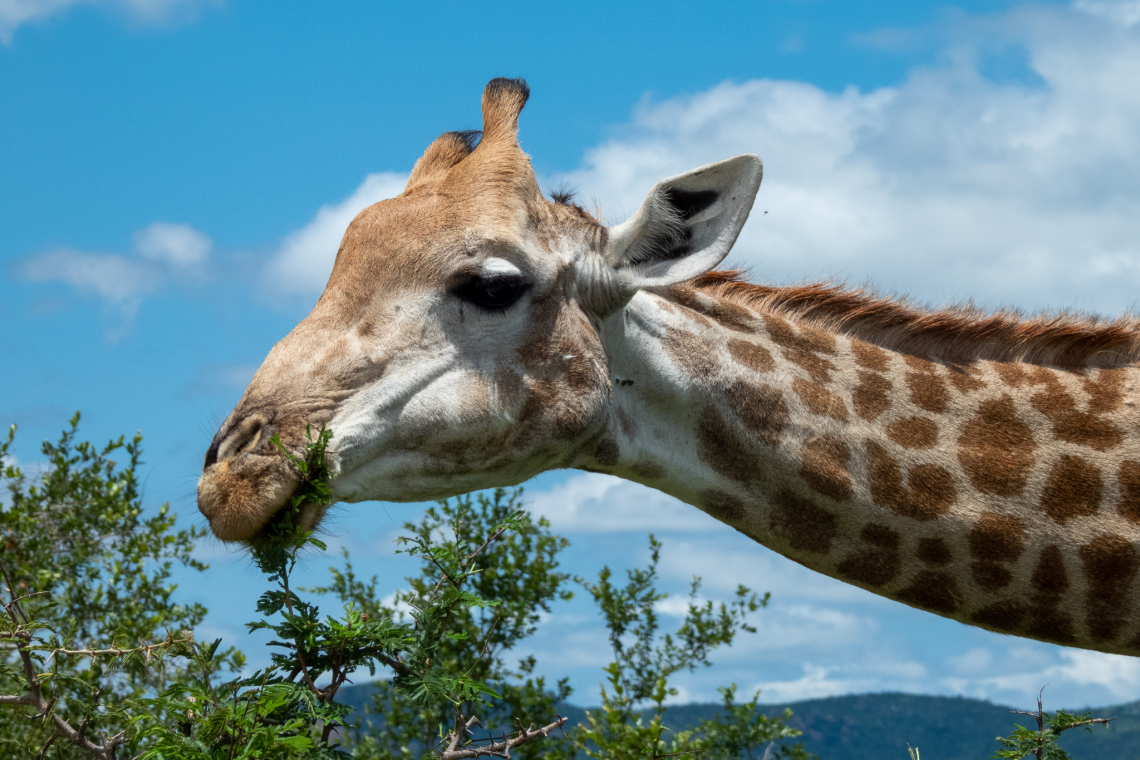
Towering above the open plains, grass and woodlands of Africa, giraffes, with their extremely long necks and legs, are the world’s tallest mammals. They are social animals that roam the savannah peacefully in large herds as they forage for food at the tops of trees. Handsome and impressive yet awkward, no safari would be complete without these gentle giants.
They certainly stand out from the crowd, but they are in danger and have been listed as vulnerable by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). As Africa’s development escalates with increased agricultural activities, settlements expanding, and more roads being constructed, the giraffe population is shrinking as they are losing their favourite acacia trees that are their main food source.What are the giraffe species and subspecies?
Although giraffes are among the world’s most recognised animals of the savannah, they have been taken for granted for too long and have been vastly under-researched. It had been widely recognised that according to the IUCN that the giraffe was one species Giraffa Camelopardalis, with nine subspecies.
However, the Giraffe Conservation Foundation (GCF) has performed DNA analyses and sampling and has updated its taxonomy showing four distinct species and five subspecies. For this study, the GCF team collected tissue samples from 190 wild giraffes. These were collected by remote biopsy darts—darts that immediately pop off the animal after impact, taking a small piece of tissue with them. By using this method, the giraffes did not need to be sedated.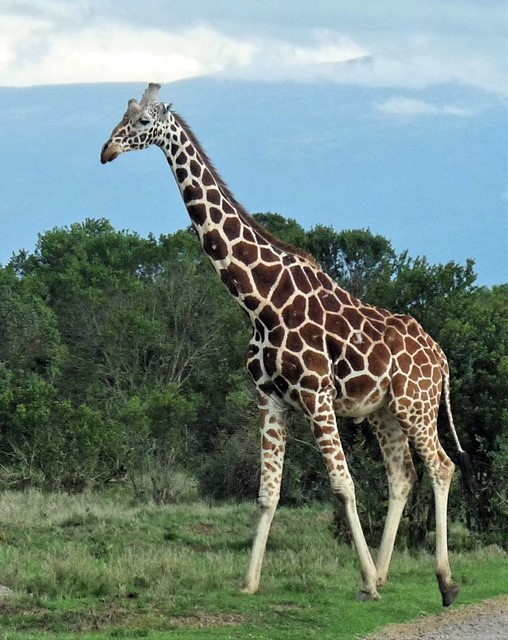
Reticulated Giraffe
The samples collected by GCF over 15 years included tissue from all major giraffe populations across Africa, representing each of the nine subspecies considered to exist at that time. This is the first study to ever accomplish such a feat.
The GCF is an international science-based conservation organisation that provides innovative approaches to saving giraffes in the wild.
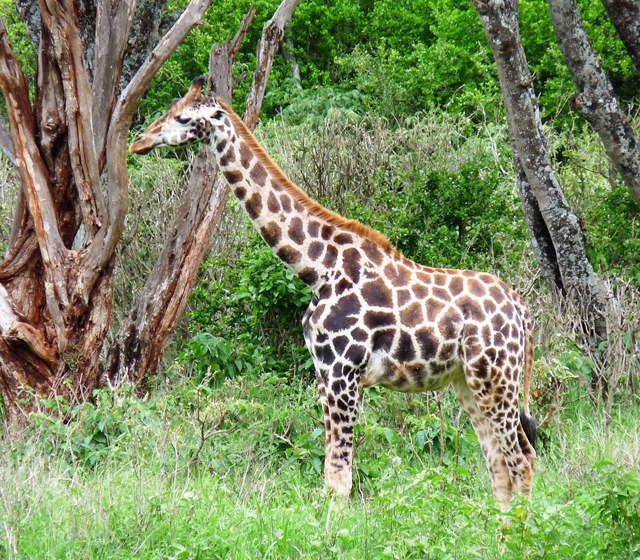

Nubian Giraffe
Current classification
The current and accurate classification method is becoming the accepted giraffe taxonomy, and according to the new study, there are four distinct species:
- Northern giraffe (Giraffa Camelopardalis)
- Southern giraffe (Giraffa giraffe)
- Masai giraffe (Giraffa tippelskirch)
- Reticulated giraffe (Giraffa reticulate)
Subspecies of the Northern giraffe:
- Nubian giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis)
- Kordofan giraffe ( antiquorum)
- West African Giraffe (Giraffa peralta)
Subspecies of the Southern giraffe
- South African giraffe(Giraffa giraffa)
- Angolan giraffe(Giraffa angolensis)
You may have wondered what happened to the Rothschild’s giraffe. It was found to be genetically identical to the Nubian giraffe, so in the current classification, it does not exist as a species or subspecies. The Thornicroft’s giraffe found in an isolated patch in Zambia was thought to be particularly vulnerable because of its small geographic distribution. However, data from the new study indicates a genetic similarity to the Masai giraffe. Whether it can be considered a subspecies or is genetically identical to the Masai giraffe will require additional research.
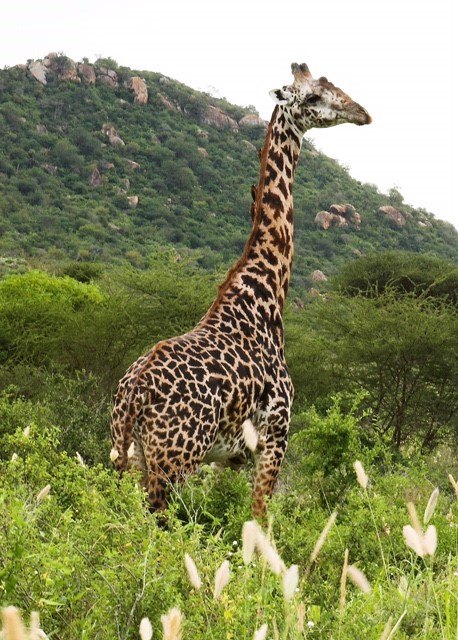

Maasai Giraffe
How to recognise the various species and where they live
Southern Giraffe: Two subspecies of the Southern giraffe occur across Southern Africa
- The South African giraffe is a common sight in South Africa, southern Botswana and Zimbabwe and is the only giraffe found in South Africa. It is brighter in colour with star or diamond-shaped markings in various shades of brown, surrounded by a light tan colour. Their lower legs are randomly speckled with uneven spots.
- Angolan giraffe no longer roams in Angola and are thought to be extinct there. Their range includes central Botswana, most parts of Namibia, and some areas of Zimbabwe. They are relatively light in colour, and in northwest Namibia, they can be almost colourless. They have large, uneven and irregular light brown patches surrounded by a pale cream colour, and their lower legs are randomly speckled with uneven spots.
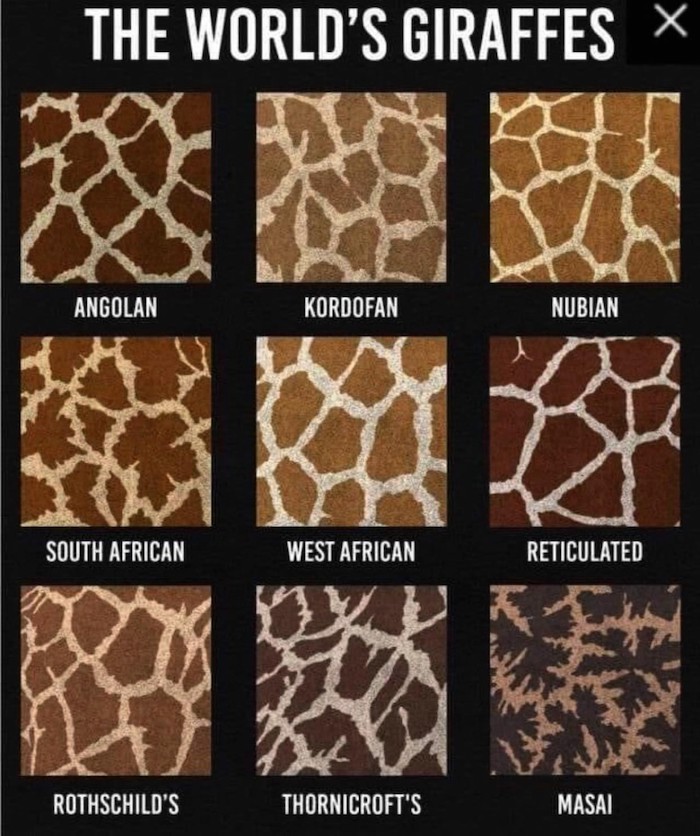

Giraffe Coat Pattern
Masai Giraffe are widely seen in Kenya and Tanzania and is the largest population of giraffe in Africa. They are Africa’s darkest giraffe, and their markings have a distinct dark brown colour against a reddish/orange background. The markings are jagged with shapes resembling veined leaves. The Masai giraffe’s legs are partially covered by patterns but remain a dark colour, unlike other giraffe species, which are known for their cream-coloured legs.
Reticulated Giraffe are found in Kenya, Somalia and Ethiopia, although the Kenya populations are the best protected. They are easily recognised by their brown-orange markings, which are well defined by a network of white lines in a brick-like or netted pattern, called a reticulated pattern which gives them their name.

West African Giraffe
Northern Giraffe has three subspecies found across Western, Central and Eastern Africa.
- Nubian giraffe is the first giraffe species ever recorded, and the name refers to the nominate species meaning the one discovered first. The Nubian giraffe includes the genetically identical formerly recognised Rothschild’s giraffe. They are found in small groups in Kenya, Uganda, Ethiopia and South Sudan. The Nubian giraffe’s patches are large, rectangular and chestnut-brown and surrounded by an off-white colour. There are no spots on the legs.
- Kordofan giraffe lives in Africa’s most hostile regions: Southern Chad, the Central African Republic and the northern parts of the DRC. It has a yellowish-brown to blackish-brown coat with pale markings that are wide and irregular, extending down its legs.
- West African Giraffe were once widespread across West Africa but are now only found in Niger. It has light tan-coloured spots and pale cream-coloured legs.
What would Africa be without the giraffe? They are vital to keeping ecosystems in balance as they eat the browse that others cannot reach, which promotes the growth of forage and opens areas for themselves and other smaller browsers. Giraffe’s lives are so intertwined with acacia trees that some seedlings do not germinate until they have passed through the giraffe’s digestive system.
Next time you are on safari, know how to identify these species and subspecies and what each species-specific conservation concerns are, and the important role they play in the environment where they live. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has found that all giraffes are vulnerable, indicating they are at a high risk of extinction in the wild.


